Our eyes and vision are one of the most important senses we have to take in the world around us. It can be scary when we start noticing symptoms that pose a risk to our sight.
Dry eyes are a common condition that can cause discomfort and even vision loss. The eye constantly produces tears to reduce friction and keep vision sharp. Some people are unable to produce normal tears or their tears evaporate too quickly.
When this happens, it can cause pain and vision problems. If you are experiencing symptoms it’s important to schedule an eye exam.
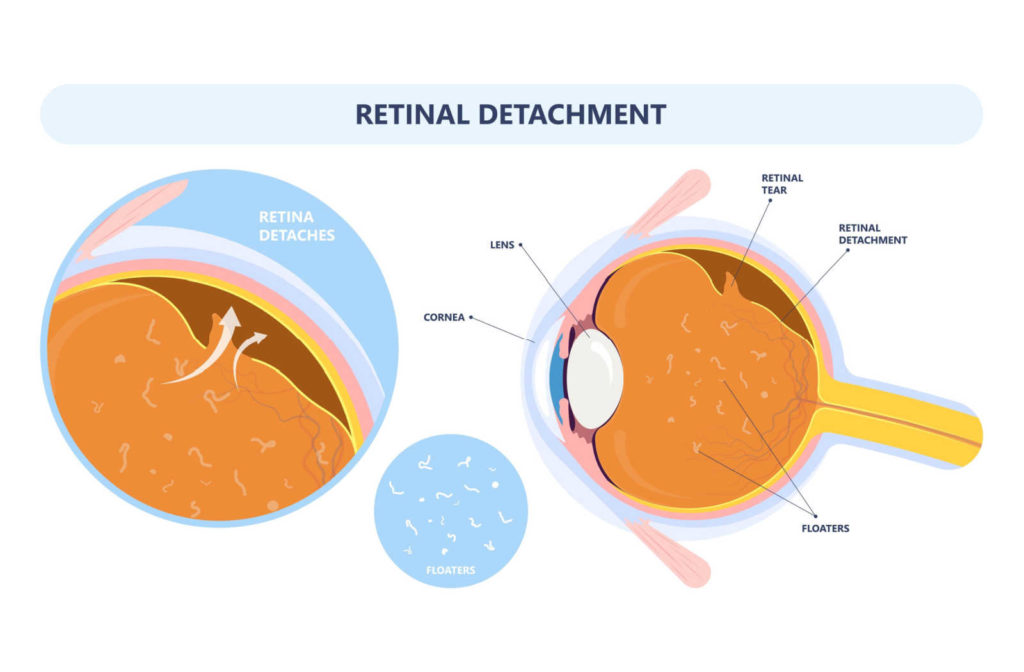
Retinal detachment can be caused by many things, it happens when your retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of your eye) is pushed out of its normal position.
You may not notice any symptoms if only a small portion of your retina has detached. However, if more of your retina is detached, you may not be able to see as clearly as usual, and you may experience other unexpected symptoms.
There are some similarities between the symptoms of both of these ocular health problems. Because of this, many people wonder if their dry eye disease can be the cause of retinal detachment. Let’s learn a little bit more about both conditions.
What is Dry Eye Disease?
Chronic dry eye is a condition in which your eyes either produce insufficient tears or tears of poor quality. It can be irritating, causing symptoms such as:
- Stringy mucus in or around your eyes
- Light sensitivity
- Eye Redness
- Floaters & Flashes
- Eye strain or blurred vision
- Stinging or burning of the eyes
- Eye fatigue, especially after using a computer, phone, or reading for an extended period
- The feeling that something is in your eyes
- Difficulty wearing contacts
- Crusting in the eyes and puffy, reddened eyelids.
You may also wake up with irritated eyes regularly. The severity of dryness varies from person to person.
However, if your dry eye doesn’t go away or is intensifying, it’s time to seek additional treatment.
Dry eye disease becomes more likely as you get older. According to the Women’s Health Study and the Physician’s Health Study, the incidence of dry eye disease increases in men and women every five years after the age of 50, with women having a higher prevalence than men.
What is a Retinal Detachment?
Retinal detachment is a medical emergency in which a thin layer of tissue at the back of the eye (the retina) pulls away from its normal position.
Retinal detachment occurs when the retinal cells become detached from the layer of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nourishment to the eye. The longer you wait to treat a retinal detachment, the greater your risk of permanent vision loss in the affected eye.
One or more of the following symptoms may indicate retinal detachment:
- The sudden appearance of a large number of floaters
- Light flashes in one or both eyes
- Blurry Vision
- Reduced peripheral vision
- A curtain-like shadow across your field of vision.
There are numerous causes of retinal detachment, but the two most common are aging and eye injury.

Can Dry Eye Disease Cause Retinal Detachment?
You’ve likely noticed through reading this blog a few similarities between dry eye disease and retinal detachment. Both can cause you to see floaters or flashes in your line of sight, as well as blurry vision. But does this mean that dry eye disease can cause a retinal detachment?
Both eye issues are just possible side effects of aging. One will not cause the other and fortunately, there are steps you can make to lower your risk of each.
Lowering Your Risk of Dry Eye & Retinal Detachment
Most people who suffer from occasional or mild dry eyes can get by with over-the-counter eyedrops (artificial tears). You have other options if your symptoms are severe and persistent such as:
- TempSure Envi
- Eyelid cleansers
- PRN De3 Dry Eye Omega Benefits
- Hypochlorous lid spray
- Eye drops and medications
- MiBoFLo
The cause of your dry eyes will determine what you do. Some treatments aim to treat or reverse the condition that’s causing your dry eyes. Other treatments can help to improve the quality of your tears or keep them from evaporating too quickly.
Because retinal detachment is commonly caused by aging, there is often no way to avoid it. However, you can reduce your risk of retinal detachment from an eye injury by wearing safety goggles or other protective eye gear when engaging in high-risk activities such as sports.
Worried about retinal detachment and dry eye?
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms of dry eye disease or retinal detachment, it’s best to book an appointment to see your eye doctor as soon as possible. Early detection is key to managing any ocular health issues you may be experiencing.